以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释
@since JDK1.0以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码注释
@since 1.2
可以看出,HashTable比HashMap要早一点出来(老一些)。
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释* @author Arthur van Hoff* @author Josh Bloch* @author Neal Gafter以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码注释* @author Doug Lea* @author Josh Bloch* @author Arthur van Hoff* @author Neal Gafter
HashMap和Hashtable的区别,可以看到,HashMap比HashTable多一个 Doug Lea 的作者,想知道Doug Lea大神的信息,简介如下:
--------------------来自百度百科
如果IT的历史,是以人为主体串接起来的话,那么肯定少不了Doug Lea。这个鼻梁挂着眼镜,留着德王威廉二世的胡子,脸上永远挂着谦逊腼腆笑容,服务于纽约州立大学Oswego分校计算机科学系的老大爷。
说他是这个世界上对Java影响力最大的个人,一点也不为过。因为两次Java历史上的大变革,他都间接或直接的扮演了举足轻重的角色。2004年所推出的Tiger。Tiger广纳了15项JSRs(Java Specification Requests)的语法及标准,其中一项便是JSR-166。JSR-166是来自于Doug编写的util.concurrent包。
值得一提的是: Doug Lea也是JCP (Java社区项目)中的一员。
Doug是一个无私的人,他深知分享知识和分享苹果是不一样的,苹果会越分越少,而自己的知识并不会因为给了别人就减少了,知识的分享更能激荡出不一样的火花。《Effective JAVA》这本Java经典之作的作者Joshua Bloch便在书中特别感谢Doug Lea是此书中许多构想的共鸣板,感谢Doug Lea大方分享丰富而又宝贵的知识。
首先,现在面试还在问:【HashMap和HashTable的区别】的情况比较少了,这是比较老的面试题,因为
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释* Java Collections Framework</a>. Unlike the new collection* implementations, {@code Hashtable} is synchronized. If a* thread-safe implementation is not needed, it is recommended to use* {@link HashMap} in place of {@code Hashtable}. If a thread-safe* highly-concurrent implementation is desired, then it is recommended* to use {@link java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap} in place of* {@code Hashtable}.
简单翻译就是说,就是 HashTable已经淘汰了 , 如果不需要线程安全,那么使用HashMap代替HashTable,如果你需要线程那么使用ConcurrentHashMap代替HashTable。
如果现在问到这块,回答的应该要更加全面,比如:
【版本】-->【作者】-->【继承】-->【安全】-->【数据结构】-->【算法】
这样的回答,已经很漂亮,当然,还可以更好,HashTable安全是如何做到的的,HashMap为什么支持null,HashCode重复了怎么办,这些,往后看。
HashMap和HashTable 都是给予哈希来实现键值映射的工具类。下面是他们的继承、实现的关系。
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{}public abstract class Dictionary<K,V> {}以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码注释
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable{}public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {}
从源码中可以看出,他们继承的体系又一些不同,虽然都是实现了Map、Cloneable、Serializable三个接口,但是HashMap继承抽象类 AbstractMap,HashTable继承抽象类Dictionary,这里提一下,Dictionary类是一个已经被废弃的类,这一点在注释中有写:
以下内容来自java.util.Dictionary* <strong>NOTE: This class is obsolete. New implementations should* implement the Map interface, rather than extending this class.</strong>
细节上还有一点,Dictionary这个类,多一个方法,elements,但是介于 Dictionary已经废弃了,我也就没有在关注他了。
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {// Make sure the value is not null.........}
public synchronized Enumeration<K> keys() {return this.<K>getEnumeration(KEYS);}以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码
public V put(K key, V value) {return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);}
public V get(Object key) {Node<K,V> e;return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;}
可见,HashTable 线程安全的做法,比较简单,就是所有方法都是带 synchronized 。
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {// Make sure the value is not nullif (value == null) { // 这里会抛错throw new NullPointerException();}// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;int hash = key.hashCode();//如果key为null,这里会报NullPointerException........................}以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码, jdk1.7版本public V put(K key, V value) {if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {inflateTable(threshold);}if (key == null)return putForNullKey(value);//这里做了特殊处理int hash = hash(key);int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {Object k;if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {V oldValue = e.value;e.value = value;//Value 直接赋值,不会报错,作为 Null 存入Mape.recordAccess(this);return oldValue;}}modCount++;addEntry(hash, key, value, i);return null;}/*** Offloaded version of put for null keys*/private V putForNullKey(V value) {for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {if (e.key == null) {// 把null 作为 一个key 存在 table[0]的位子V oldValue = e.value;e.value = value;e.recordAccess(this);return oldValue;}}modCount++;addEntry(0, null, value, 0);return null;}
通过源码可以看出:
Map map = new HashMap();System.out.println(map.size());System.out.println(map.put("a","a"));System.out.println(map.size());System.out.println(map.put("a",null));System.out.println(map.size());System.out.println(map.put("a","a"));System.out.println(map.size());输出结果:0null1 //size 是1 a1//size 还是1null1//size 还是1
从测试代码可以看出,size,一直是1,map的大小并没有发生改变。
在就是到了Jdk1.8,HashMap的变化还是有非常大的,如下:
以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码 JDK1.8/*** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.** <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)** <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to* distinguish these two cases.** @see #put(Object, Object)*/public V get(Object key) {Node<K,V> e;return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;}/*** Implements Map.get and related methods** @param hash hash for key* @param key the key* @return the node, or null if none*/final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))return first;if ((e = first.next) != null) {if (first instanceof TreeNode)return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);do {if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))return e;} while ((e = e.next) != null);}}return null;}/*** Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old* value is replaced.** @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated* @param value value to be associated with the specified key* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)*/public V put(K key, V value) {return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);}/*** Implements Map.put and related methods** @param hash hash for key* @param key the key* @param value the value to put* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.* @return previous value, or null if none*/final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)n = (tab = resize()).length;if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);else {Node<K,V> e; K k;if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;else if (p instanceof TreeNode)e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);else {for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {if ((e = p.next) == null) {p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))break;p = e;}}if (e != null) { // existing mapping for keyV oldValue = e.value;if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)e.value = value;afterNodeAccess(e);return oldValue;}}++modCount;if (++size > threshold)resize();afterNodeInsertion(evict);return null;}一眼看去,代码复杂很多,简单的说,JDK1.8对HashMap进行了较大的优化,底层实现由之前的“数组+链表”改为“数组+链表+红黑树”。我这里不详细展开,有兴趣的,可以看一下:https://blog.csdn.net/v123411739/article/details/78996181
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释/*** The hash table data.*/private transient Entry<K,V>[] table; // 这个对象/*** Constructs a new, empty hashtable with the specified initial* capacity and the specified load factor.** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hashtable.* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hashtable.* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive.*/public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);if (initialCapacity==0)initialCapacity = 1;this.loadFactor = loadFactor;table = new Entry[initialCapacity];threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);initHashSeedAsNeeded(initialCapacity);}以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码注释/*** An empty table instance to share when the table is not inflated.*/static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};/*** The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.*/transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;// 这个对象HashMap和HashTable都是用哈希表来存储键值对,在数据结构上基本相同的,从源码中可以看到,都是建立了一个 【transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;】,Map.Entry是一个私有内部类,每一个Entry对象表示存储在Hash表中的一个键值对。
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {int hash;//hash键对象的hash值final K key;//key对象V value;//值对象Entry<K,V> next;//指链表中下一个Entry对象,可为null,表示当前Entry对象在链表尾部。
可以说,有多少个键值对,就有多少个Entry对象,那么在HashMap和HashTable中是怎么存储这些Entry对象,以方便我们快速查找和修改的呢?请看下图。
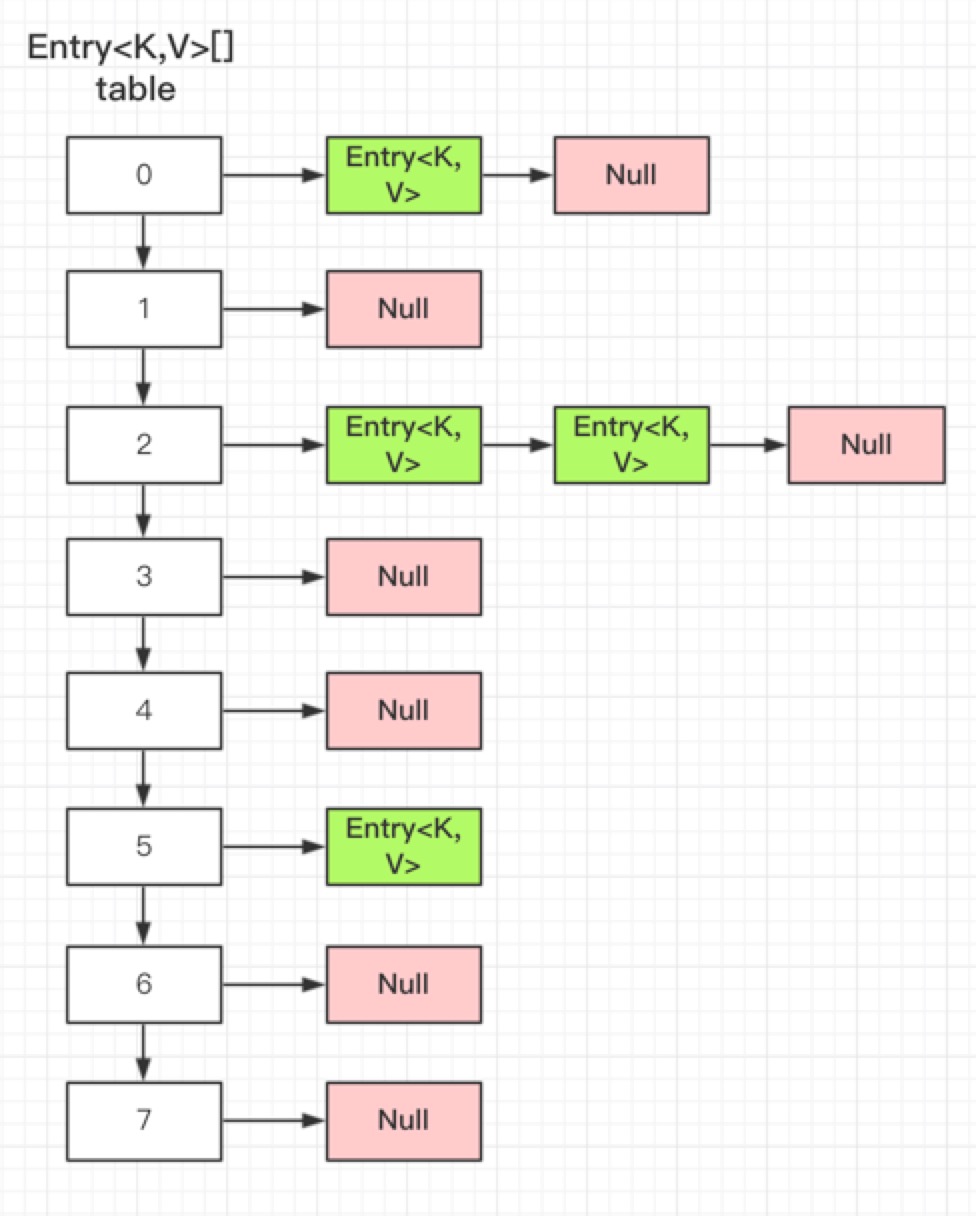
上图画出的是一个桶数量为8,存有4个键值对的HashMap/HashTable的内存布局情况。可以看到HashMap/HashTable内部创建有一个Entry类型的引用数组,用来表示哈希表,数组的长度,即是哈希桶的数量。而数组的每一个元素都是一个Entry引用,从Entry对象的属性里,也可以看出其是链表的节点,每一个Entry对象内部又含有另一个Entry对象的引用。
哈希碰撞就是上图 【2】的位子,两个 Entry的hash值计算出来,在同一个位子上。
这样就可以得出结论,HashMap/HashTable内部用Entry数组实现哈希表,而对于映射到同一个哈希桶(数组的同一个位置)的键值对,使用Entry链表来存储(解决hash冲突)。
这里照顾一下新人:java 的transient关键字为我们提供了便利,你只需要实现Serilizable接口,将不需要序列化的属性前添加关键字transient,序列化对象的时候,这个属性就不会序列化到指定的目的地中。
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释/*** Constructs a new, empty hashtable with a default initial capacity (11)* and load factor (0.75).*///初始化 11public Hashtable() {this(11, 0.75f);}/*** Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this* hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more* efficiently. This method is called automatically when the* number of keys in the hashtable exceeds this hashtable's capacity* and load factor.*/protected void rehash() {int oldCapacity = table.length;Entry<K,V>[] oldMap = table;// overflow-conscious code 乘2+1int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;。。。。。。。。。。。。。。}以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码注释/*** The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.*///初始化1 左移4次, 2的四次方,16 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16/*** Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this* method to resize the table if appropriate.** Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.*/void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {resize(2 * table.length);//每次扩容,乘2hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);}createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);}HashTable初始化大小是11,每次扩容是原来的2n+1,如果用户输入大小,就会直接设定用户输入的大小。
HashMap的初始化大小是16,每次扩容是原来的两倍,如果用户输入大小,HashMap会默认将其阔充到2的幂次。
HashTable的做法是尽量使用素数、奇数,这样做,简单的取模哈希的结果会更加平均。
HashMap的优势,在于取模计算是,如果模数是2的幂,那么我们可以直接使用位运算来得到结果,效率要大大高于做除法。
以下内容来自java.util.HashTable源码注释
/*** A randomizing value associated with this instance that is applied to* hash code of keys to make hash collisions harder to find.*/transient int hashSeed;private int hash(Object k) {// hashSeed will be zero if alternative hashing is disabled.return hashSeed ^ k.hashCode();}以下内容来自java.util.HashMap源码注释int hash = hash(key);int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);// 在计算了key.hashCode()之后,做了一些位运算来减少哈希冲突final int hash(Object k) {int h = hashSeed;if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);}h ^= k.hashCode();// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);}/*** Returns index for hash code h.*/static int indexFor(int h, int length) {// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";return h & (length-1);}
正如我们所言,HashMap由于使用了2的幂次方,所以在取模运算时不需要做除法,只需要位的与运算就可以了。但是由于引入的hash冲突加剧问题,HashMap在调用了对象的hashCode方法之后,又做了一些位运算在打散数据。关于这些位计算为什么可以打散数据的问题,本文不再展开了。
如果你有细心读代码,还可以发现一点,就是HashMap和HashTable在计算hash时都用到了一个叫hashSeed的变量。这是因为映射到同一个hash桶内的Entry对象,是以链表的形式存在的,而链表的查询效率比较低,所以HashMap/HashTable的效率对哈希冲突非常敏感,所以可以额外开启一个可选hash(hashSeed),从而减少哈希冲突。因为这是两个类相同的一点,所以本文不再展开了,感兴趣的看这里。事实上,这个优化在JDK 1.8中已经去掉了,因为JDK 1.8中,映射到同一个哈希桶(数组位置)的Entry对象,使用了红黑树来存储,从而大大加速了其查找效率。
版权声明:本站所有资料均为网友推荐收集整理而来,仅供学习和研究交流使用。

工作时间:8:00-18:00
客服电话
电子邮件
admin@qq.com
扫码二维码
获取最新动态
