12月23-24日

在数据分析和机器学习的一些任务里面,对于数据集的某些列或者行丢弃,以及数据集之间的合并操作是非常常见的.
Python数据预处理?
1、合并操作
pandas.merge(left, right, how=’inner’, on=None, left_on=None, right_on=None, left_index=False, right_index=False, sort=False, suffixes=(‘_x’, ‘_y’), copy=True, indicator=False)
python的pandas模块。
作用:通过执行一个类似于数据库风格join的操作,来在columns(列)或者indexes(行)上合并DataFrame对象. 如果在columns和columns上面进行join,那么indexes就会被忽略.同样,要是在indexes和indexes之间或者indexes和columns之间进行join,那么index也会被忽略.
参数:
left : DataFrame
right : DataFrame
how : {‘left’, ‘right’, ‘outer’, ‘inner’}, default ‘inner’
left: use only keys from left frame (SQL: left outer join)
right: use only keys from right frame (SQL: right outer join)
outer: use union of keys from both frames (SQL: full outer join)
inner: use intersection of keys from both frames (SQL: inner join)
on : label or list
Field names to join on. Must be found in both DataFrames. If on is None and not merging on indexes, then it merges on the intersection of the columns by default.
left_on : label or list, or array-like
Field names to join on in left DataFrame. Can be a vector or list of vectors of the length of the DataFrame to use a particular vector as the join key instead of columns
right_on : label or list, or array-like
Field names to join on in right DataFrame or vector/list of vectors per left_on docs
left_index : boolean, default False
Use the index from the left DataFrame as the join key(s). If it is a MultiIndex, the number of keys in the other DataFrame (either the index or a number of columns) must match the number of levels
right_index : boolean, default False
Use the index from the right DataFrame as the join key. Same caveats as left_index
sort : boolean, default False
Sort the join keys lexicographically in the result DataFrame
suffixes : 2-length sequence (tuple, list, …)
Suffix to apply to overlapping column names in the left and right side, respectively
copy : boolean, default True
If False, do not copy data unnecessarily
indicator : boolean or string, default False
If True, adds a column to output DataFrame called “_merge” with information on the source of each row. If string, column with information on source of each row will be added to output DataFrame, and column will be named value of string. Information column is Categorical-type and takes on a value of “left_only” for observations whose merge key only appears in ‘left’ DataFrame, “right_only” for observations whose merge key only appears in ‘right’ DataFrame, and “both” if the observation’s merge key is found in both.
New in version 0.17.0.
Returns:
merged : DataFrame
The output type will the be same as ‘left’, if it is a subclass of DataFrame.
2、丢弃操作
python数据处理模块、
DataFrame.drop(labels, axis=0, level=None, inplace=False, errors=’raise’)
作用:返回一个指定轴上label被移除之后的对象。
参数:
labels : 一个或者一列label值
axis : int类型或者轴的名字,这个轴和labels配合起来,比如,当axis=0的时候,就是行上面的label,当axis=1的时候,就是列上面的label
level : int or level name, default None
For MultiIndex
inplace : bool, 默认是False,这个表示是不是在原始的dataframe上面做替换。要是是Ture的话,原始dataframe会变化,同时返回的是None。
errors : {‘ignore’, ‘raise’},默认是‘raise’。要是是‘ignore’的话,就不管error,已经存在的labels会被丢弃。
pandas处理excel数据?
例子:
import numpy as np
pandas数据匹配,import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['a', 'b', 'a'], 'B': ['b', 'a', 'c'],
'C': [1, 2, 3]})
print("original:\n",df)
pandas数据分析实例、#get1接受的是第0行(因为这个时候axis=0)移除之后的新对象
#因为inplace默认是False,所以df不会有变化
get1=df.drop(labels=0)
print("df:\n",df)
pandas模块,print("get1:\n",get1)
#因为inplace这时候是True,所以df会变化,同时get2接受的是None值
get2=df.drop(labels=0,inplace=True)
print("df:\n",df) print("get1:\n",get2)
pandas怎么安装,#这个时候是移除列了,对比上面来看
get3=df.drop(labels="A",axis=1)
print("df:\n",df)
print("get3:\n",get3)
pandas怎么用。
结果: 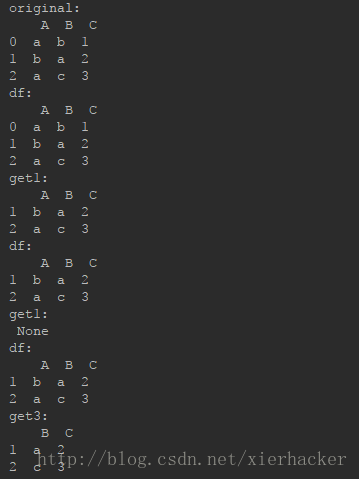
DataFrame.pop(item)
numpy和pandas安装,
作用:返回这个item,同时把这个item从frame里面丢弃。
3、编码
把类别量装换为指示变量(其实就是one-hot encoding)
pandas.get_dummies(data, prefix=None, prefix_sep=’_’, dummy_na=False, columns=None, sparse=False, drop_first=False)
参数:
data : 类array类型,Series或者是DataFrame类型.
prefix : 字符串,或者字符串列表,或者字符串字典.默认为None,这里应该传入一个字符串列表,且这个列表的长度是和将要被get_dummis的那些列数量是相等的.同样,prefix选项也可以是一个把列名映射到prefixes的字典.
prefix_sep : string, default ‘_’
If appending prefix, separator/delimiter to use. Or pass a list or dictionary as with prefix.
dummy_na : bool, default False
Add a column to indicate NaNs, if False NaNs are ignored.
columns : list-like, default None
Column names in the DataFrame to be encoded. If columns is None then all the columns with object or category dtype will be converted.
sparse : bool, default False
Whether the dummy columns should be sparse or not. Returns SparseDataFrame if data is a Series or if all columns are included. Otherwise returns a DataFrame with some SparseBlocks.
New in version 0.16.1.
drop_first : bool, default False
Whether to get k-1 dummies out of k categorical levels by removing the first level.
New in version 0.18.0.
Returns
——-
dummies : DataFrame or SparseDataFrame
例1.Series
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
#对于一个Series来说,行数保持不变,列数变为不同类的个数
#但是每一行还是以编码的形式表示原来的类别
#这个函数返回是一个DataFrame,其中列名为各种类别
s = pd.Series(list('abca'))
print("original:")
print(s)
print("get dummy:")
s_dummy=pd.get_dummies(data=s)
print(s_dummy)
print("type of s_dummy:",
type(s_dummy))
结果: 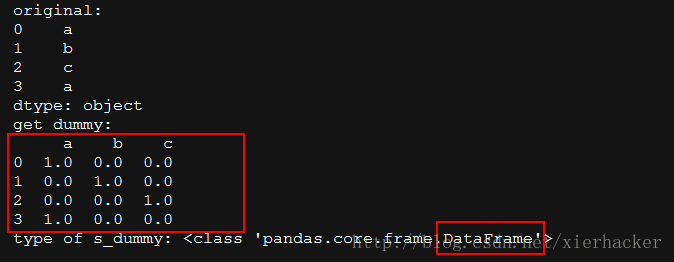
例2.DataFrame
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['a', 'b', 'a'], 'B': ['b', 'a', 'c'],
'C': [1, 2, 3]})
print("original:")
print(df)
#其中只要是类别相关的,都会被hot-encoding
#每一个特征(原始形式的列名)下面有几种不同的类别,就会生成几列(比如A下面只有a和b两种形式,就会生成A_a和A_b两列)
#原始为数字的那些特征,保持不变
#prefix表示你对于新生成的那些列想要的前缀,你可以自己命名
df_dummy=pd.get_dummies(data=df,prefix=["A","B"])
print("get dummy:")
print(df_dummy)
结果: 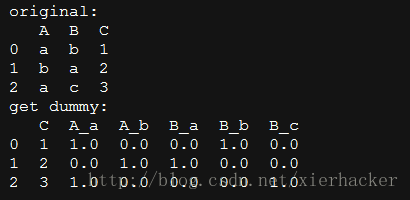
4、处理缺失值
pandas使用浮点数NaN(not a number)表示浮点和非浮点数组中的缺失数据.
pandas中,自己传入的np.nan或者是python内置的None值,都会被当做NaN处理,如下例.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
s=pd.Series(data=["tom","jack","kate",np.nan])
print(s)
s[0]=None
print(s)
结果: 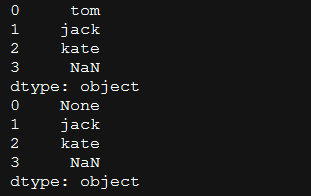
DataFrame.isnull()
作用,返回一个和原来DataFrame一样形状的,里面值为布尔型的DataFrame.
例子:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
s=pd.Series(data=["tom","jack","kate",np.nan])
print(s)
print(s.isnull())
print(type(s.isnull()))
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['a', 'b', np.nan], 'B': ['b', 'a', 'c'],
'C': [1, 2, np.nan]})
print("original:")
print(df)
print(df.isnull())
结果: 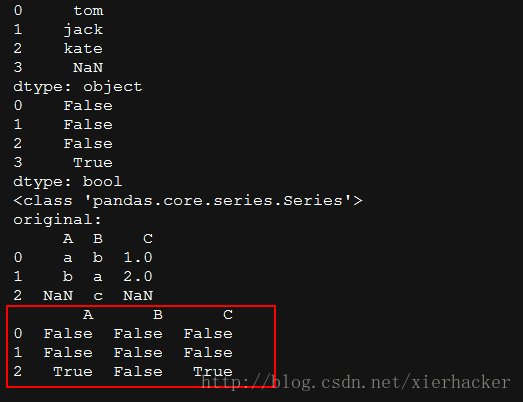
使用指定的方法来填充缺失值,并且返回被填充好的DataFrame
DataFrame.fillna(value=None,method=None,axis=None,inplace=False,limit=None,downcast=None, **kwargs)
参数:
value : 可以是标量,字典,Series对象,DataFrame对象.value的作用就是用来填充那些缺失的部分.
method : 可选为{‘backfill’, ‘bfill’, ‘pad’, ‘ffill’, None}, 默认是None,
Method to use for filling holes in reindexed Series pad / ffill: propagate last valid observation forward to next valid backfill / bfill: use NEXT valid observation to fill gap
axis : {0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’}
inplace : 布尔值,默认为False.要是为True的话,那么就会就地修改.
limit : (对于前向填充和后向填充)可以连续填充的最大数量.
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/xierhacker/article/details/65935459
查阅更为简洁方便的分类文章以及最新的课程、产品信息,请移步至全新呈现的“LeadAI学院官网”:
www.leadai.org
请关注人工智能LeadAI公众号,查看更多专业文章

大家都在看
LSTM模型在问答系统中的应用
基于TensorFlow的神经网络解决用户流失概览问题
最全常见算法工程师面试题目整理(一)
最全常见算法工程师面试题目整理(二)
TensorFlow从1到2 | 第三章 深度学习革命的开端:卷积神经网络
装饰器 | Python高级编程
今天不如来复习下Python基础

点击“阅读原文”直接打开报名链接
版权声明:本站所有资料均为网友推荐收集整理而来,仅供学习和研究交流使用。

工作时间:8:00-18:00
客服电话
电子邮件
admin@qq.com
扫码二维码
获取最新动态
