libxml(一)
讀取xml文件、?
摘要?
Libxml是個有免費許可的用于處理XML、能輕松跨越多個平臺的C語言庫。這個指南提供他的基本函數的例子。
緒論?
Libxml是個實現讀、創建及操縱XML數據功能的C語言庫。這個指南提供例子代碼并給出他基本功能的解釋。在這個項目的主頁上有Libxml及更多關于他可用的資料。包含有完整的API文件。這個指南并不能替代這些完整的文件,不過闡明功能需要使用庫來完成基本操作。?
? ?這個指南基于一個簡單的XML應用,他使用我寫的一篇文章生成,他包含有元數據和文章的主體。
本指南中的例子代碼示范怎么做到:?
• 解析文件?
• 取得指定元素的文本?
• 添加一個元素及他的內容?
• 添加一個屬性?
• 取得一個屬性的值?
例子的完整代碼包含在附錄中?
?
數據類型?
Libxml定義了許多數據類型,我們將反復碰到他們,他隱藏了雜亂的來源以致你不必處理他除非你有特定的需要。xmlChar ?替代char,使用UTF-8編碼的一字節字符串。如果你的數據使用其他編碼,他必須被轉換到UTF-8才能使用libxml的函數。在libxml編碼支持WEB頁面有更多關于編碼的有用信息。?
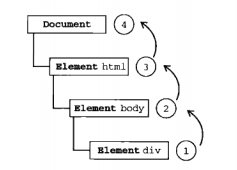
XmlDoc 包含由解析文件建立的樹結構,xmlDocPtr是指向這個結構的指針。
xmlNodePtr and xmlNode 包含單一結點的結構xmlNodePtr是指向這個結構的指針,他被用于遍歷文件樹。?
?
解析文件?
解析文件時僅僅需要文件名并只調用一個函數,并有錯誤檢查。完整代碼:附錄C, Keyword例程代碼?
?
①xmlDocPtr doc;?
②xmlNodePtr cur;?
③doc = xmlParseFile(docname);?
④if (doc == NULL ) {?
fprintf(stderr,"Document not parsed successfully. \n");?
return;?
}?
⑤cur = xmlDocGetRootElement(doc);?
⑥if (cur == NULL) {?
fprintf(stderr,"empty document\n");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
}?
⑦if (xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *) "story")) {?
fprintf(stderr,"document of the wrong type, root node != story");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
}?
①定義解析文件指針。?
②定義結點指針(你需要他為了在各個結點間移動)。?
④檢查解析文件是否成功,如果不成功,libxml將指一個注冊的錯誤并停止。?
?
注釋?
一個常見錯誤是不適當的編碼。XML標準文件除了用UTF-8或UTF-16外還可用其他編碼保存。如果文件是這樣,libxml將自動地為你轉換到UTF-8。更多關于XML編碼信息包含在XML標準中。?
⑤取得文件根元素?
⑥檢查確認當前文件中包含內容。?
⑦在這個例子中,我們需要確認文件是正確的類型。“Story”是在這個指南中使用文件的根類型。?
?
取得元素內容?
?
你找到在文件樹中你要查找的元素后能取得他的內容。在這個例子中我們查找“story”元素。進程將在冗長的樹中查找我們感興趣的元素。我們假定期你已有了一個名為doc的xmlDocPtr和一個名為cur的xmlNodPtr。?
①cur = cur->xmlChildrenNode;?
②while (cur != NULL) { ??
if ((!xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *)"storyinfo"))){?
parseStory (doc, cur);?
}?
cur = cur->next;?
}?
?
①取得cur的第一個子結點,cur指向文件的根,即“story”元素。?
②這個循環迭代通過“story”的子元素查找“storyinfo”。這是個包含有我們將查找的“keywords”的元素。他使用了libxml字符串比較函數xmlStrcmp。如果相符,他調用函數parseStory。?
?
void?
parseStory (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlNodePtr cur) {?
xmlChar *key;?
① cur = cur->xmlChildrenNode;?
②while (cur != NULL) {?
if ((!xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *)"keyword"))) {?
③ key = xmlNodeListGetString(doc, cur->xmlChildrenNode, 1);?
printf("keyword: %s\n", key);?
xmlFree(key);?
}?
cur = cur->next;?
}?
return;?
}?
① 再次取得第一個子結點。?
② 像上面那個循環相同,我們能過迭代,查找我們感興趣的叫做“keyword”的元素。?
③ 當我們找到元素“keyword”時,我們需要打印他包含在XML中的記錄的內容,文本被包含于元素的子結點中,因此我們借助了cur->xmlChildrenNode,為了取得文本,我們使用函數xmlNodeListGetString,他有一個文件指針參數,在這個例子中,我們僅僅打印他。?
注釋?
因為xmlNodeListGetString為他返回的字符串分配內存,你必須使用xmlFree釋放他。?
?
使用XPath取得元素內容
除了一步步遍歷文件樹查找元素外,Libxml2包含支持使用Xpath表達式取得指定結點集。完整的Xpath API文件在這里。Xpath允許通過路徑文件搜索匹配指定條件的結點。在下面的例子中,我們搜索文件中所有的“keyword”元素。?
?
注釋?
下面是Xpath完整的討論。他周詳的使用資料,請查閱Xpath規范。?
這個例子完整的代碼參見附錄D,XPath例程代碼。?
Using XPath requires setting up an xmlXPathContext and then supplying the XPath expression and the context to the xmlXPathEvalExpression?
function.?
The function returns an xmlXPathObjectPtr, which includes the set of nodes satisfying the XPath expression.?
使用XPath需要安裝xmlXPathContext才支持XPath表達式及xmlXPathEvalExpression函數,這個函數返回一個xmlXPathObjectPtr,他包含有
XPath表達式的結點集。?
?
xmlXPathObjectPtr?
getnodeset (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlChar *xpath){?
①xmlXPathContextPtr context;?
xmlXPathObjectPtr result;?
②context = xmlXPathNewContext(doc);?
③result = xmlXPathEvalExpression(xpath, context);?
④if(xmlXPathNodeSetIsEmpty(result->nodesetval)){?
printf("No result\n");?
return NULL;?
}?
xmlXPathFreeContext(context);?
return result;?
}?
①首先定義變量?
②初始化變量context?
③應用XPath表達式?
④檢查結果?
由函數返回的xmlPathObjectPtr包含一個結點集和其他需要被迭代及操作的信息。在這個例子中我們的函數返回xmlXPathObjectPtr,我們使用他打印我們文件中keyword結點的內容。這個結點集對象包含在集合(nodeNr)中的元素數目及一個結點(nodeTab)數組。?
?
①for (i=0; i nodeNr; i++) {?
②keyword = xmlNodeListGetString(doc,?
nodeset->nodeTab->xmlChildrenNode, printf("keyword: %s\n", keyword);?
xmlFree(keyword);?
}?
①變量nodeset->Nr持有結點集中元素的數量。我們使用他遍歷數組。?
②打印每個結點包含的內容。?
注釋?
Note that we are printing the child node of the node that is returned, because the contents of the keyword element are a child text node.注意我們打印的是結點的子結點的返回值,因為keyword元素的內容是個子文本結點。
寫元素?
寫元素內容使用上面許多相同的步驟?解析文件并遍歷樹。我們先解析文件然后遍歷樹查找我們想插入元素的位置。在這個例子中,我們再一次查找“storyinfo
”元素并插入一個keyword。然后我們裝文件寫入磁盤。完整代碼:附錄E,添加keyword例程?
本例中主要的不同在于parseStory?
void?
parseStory (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlNodePtr cur, char *keyword) {?
①xmlNewTextChild (cur, NULL, "keyword", keyword);?
return;?
}?
①XmlNewTextChild函數添加一個當前結點的新的子元素到樹中?
一旦結點被添加,我們應當寫文件到文件中。你是否想給元素指定一個命名空間?你能添加他,在我們的例子中,命名空間是NULL。?
?
xmlSaveFormatFile (docname, doc, 1);?
?
第一個參數是寫入文件的名,你注意到和我們剛剛讀入的文件名是相同的。在這個例子中,我們僅僅覆蓋原來的文件。第二個參數是個xmlDoc結構指針,第三個參數設定為1,確保在輸出上寫入。?
libxml(二)
?
寫屬性?
寫屬性類似于給一個新元素寫文本。在這個例子中,我們將添加一個reference結點URI屬性到我們的文件中。完整代碼:附錄F,添加屬性例程代碼。reference是story元素的一個子結點,所以找到并插入新元素及其屬性是簡單的。一旦我們在parseDoc進行了錯誤檢查,我們將在正確的位置加放我們的新元素。但進行之前我們需要定義一個此前我們不見過的數據類型。?
?
xmlAttrPtr newattr;?
?
我們也需要xmlNodePtr:?
?
xmlNodePtr newnode;?
?
剩下的parseDoc則和前面相同,檢查根結點是否為story。如果是的,那我們知道我們將在指定的位置添加我們的元素。 ??
① newnode = xmlNewTextChild (cur, NULL, "reference", NULL);?
②newattr = xmlNewProp (newnode, "uri", uri);?
?
①使用xmlNewTextChild函數添國一個新結點到當前結點位置。?
一旦結點被添加,文件應像前面的例子將我們添加的元素及文本內容寫入磁盤。?
?
取得屬性?
取得屬性值類似于前面我們取得一個結點的文本內容。在這個例子中,我們將取出我們在前一部分添加的URI的值。完整代碼:附錄G,取得屬性值例程代碼。
? ?這個例子的初始步驟和前面是類似的:解析文件,查找你感興趣的元素,然后進入一個函數完成指定的請求任務。在這個例子中,我們調用getReference。?
?
void?
getReference (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlNodePtr cur) {?
xmlChar *uri;?
cur = cur->xmlChildrenNode;?
while (cur != NULL) {?
if ((!xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *)"reference"))) {?
① uri = xmlGetProp(cur, "uri");?
printf("uri: %s\n", uri);?
xmlFree(uri);?
}?
cur = cur->next;?
}?
return;?
}?
?
① 關鍵函數是xmlGetProp,他返回一個包含屬性值的xmlChar。在本例中,我們僅僅打印他。?
?
注釋?
如果你使用DTD定義屬性的固定值或缺省值,這個函數也將取得他。?
?
編碼轉換?
數據編碼兼容問題是程式員新建普通的XML或特定XML時最常見的困難。按照這里
? ?稍后的討論來思考設計你的應用程式將幫助你避免這個困難。實際上,libxml能以UTF-8格式保存和操縱多種數據 ?
你的程式使用其他的數據格式,比如常見的ISO-8859-1編碼,必須使用libxml函數轉換到UTF-8。如果你想你的程式以除UTF-8外的其他編碼方式輸出也必須做轉換。?
? ?如果能有效地轉換數據Libxml將使用轉換器。無轉換器時,僅僅UTF-8、UTF-16和ISO-8859-1能夠被作為外部格式使用。有轉換器時,他能將從其他格式和UTF-8互換的所有格式均可使用。當前轉換器支持大約150種不同的編碼格式之間的相互轉換。實際支持的格式數量正在被實現。每一個實目前的轉換器盡可能的支持每一種格式。?
?
警告?
一個常見錯誤是在內部數據不同的部分使用不同的編碼格式。最常見的是情況是個應用以ISO-8859-1作為內部數據格式,結合libxml部分使用UTF-8格式。結果是個應用程式要面對不同地內部數據格式。一部分代碼執行后,他或其他部分代碼將使用曲解的數據。?
? ?這個例子構造一個簡單的文件,然后添加在命令行提供的內容到根元素并使用適當的編碼將結果輸出到標準輸出設備上。在這個例子中,我們使用ISO-8859-1編碼。在命令輸入的內容將被從ISO-8859-1轉換到UTF-8。完整代碼:附件H,編碼轉換例程代碼。?
?
? ?包含在例子中的轉換函數使用libxml的xmlFindCharEncodingHandler函數。?
?
①xmlCharEncodingHandlerPtr handler;?
②size = (int)strlen(in)+1;?
out_size = size*2-1;?
out = malloc((size_t)out_size);?
…?
③handler = xmlFindCharEncodingHandler(encoding);?
…?
④handler->input(out, &out_size, in, &temp);?
…?
⑤xmlSaveFormatFileEnc("-", doc, encoding, 1);?
?
①定義一個xmlCharEncodingHandler函數指針。?
②XmlCharEncodingHandler函數需要給出輸入和輸出字符串的大小,這里計算輸入輸出字符串。?
③XmlFindCharEncodingHandler使用數據初始編碼作為參數搜索libxml已完成的轉換器句柄并將找到的函數指針返回,如果沒有找到則返回NULL。?
④The conversion function identified by handler requires as its arguments pointers to the input and output strings, along with the length of each. The lengths must be determined separately by the application.?
由句柄指定的轉換函數請求輸入、輸出字符中及他們的長度作為參數。這個長度必須由應用程式分別指定。?
⑤用指定編碼而不是UTF-8輸出,我們使用xmlSaveFormatFileEnc指不定期編碼方式。 ?
?
A. 編譯?
Libxml包含一個腳本xml2-config,他一般用于編譯和鏈接程式到庫時產生標志。
? 為了取得預處理和編譯標志,使用xml2-config ?cflags,為了取得鏈接標志,使用xml2-config ?libs。其他有效的參數請使用xml2-config ?help查閱。?
?
B. 示例文件?
?
?
?
John Fleck?
June 2, 2002?
example keyword?
?
?
This is the headline?
This is the body text.?
?
?
C. Keyword例程代碼?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
void?
parseStory (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlNodePtr cur) {?
xmlChar *key;?
cur = cur->xmlChildrenNode;?
while (cur != NULL) {?
if ((!xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *)"keyword"))) {?
key = xmlNodeListGetString(doc, cur->xmlChildrenNode, 1);?
printf("keyword: %s\n", key);?
xmlFree(key);?
}?
cur = cur->next;?
}?
return;?
}?
static void?
parseDoc(char *docname) {?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
xmlNodePtr cur;?
doc = xmlParseFile(docname);?
if (doc == NULL ) {?
fprintf(stderr,"Document not parsed successfully. \n");?
return;?
}?
cur = xmlDocGetRootElement(doc);?
if (cur == NULL) {?
fprintf(stderr,"empty document\n");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
}?
if (xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *) "story")) {?
fprintf(stderr,"document of the wrong type, root node != story");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
}?
cur = cur->xmlChildrenNode;?
while (cur != NULL) {?
if ((!xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *)"storyinfo"))){?
parseStory (doc, cur);?
}?
cur = cur->next;?
}?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
}?
int?
main(int argc, char **argv) {?
char *docname;?
if (argc?
libxml(三) ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
D. XPath例程代碼?
#include ?
#include ?
xmlDocPtr?
getdoc (char *docname) {?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
doc = xmlParseFile(docname);?
if (doc == NULL ) {?
fprintf(stderr,"Document not parsed successfully. \n");?
return NULL;?
} ??
return doc;?
}?
xmlXPathObjectPtr?
getnodeset (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlChar *xpath){?
xmlXPathContextPtr context;?
xmlXPathObjectPtr result;?
context = xmlXPathNewContext(doc);?
result = xmlXPathEvalExpression(xpath, context);?
if(xmlXPathNodeSetIsEmpty(result->nodesetval)){?
printf("No result\n");?
return NULL;?
}?
xmlXPathFreeContext(context);?
return result;?
}?
int?
main(int argc, char **argv) {?
char *docname;?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
xmlChar *xpath = ("//keyword");?
xmlNodeSetPtr nodeset;?
xmlXPathObjectPtr result;?
int i;?
xmlChar *keyword;?
if (argc nodesetval;?
for (i=0; i nodeNr; i++) {?
keyword = xmlNodeListGetString(doc, nodeset->nodeTab->printf
("keyword: %s\n", keyword);?
xmlFree(keyword);?
}?
xmlXPathFreeObject (result);?
}?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
xmlCleanupParser();?
return (1);?
}?
E. 添加keyword例程代碼?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
void?
parseStory (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlNodePtr cur, char *keyword) {?
xmlNewTextChild (cur, NULL, "keyword", keyword);?
return;?
}?
xmlDocPtr?
parseDoc(char *docname, char *keyword) {?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
xmlNodePtr cur;?
doc = xmlParseFile(docname);?
if (doc == NULL ) {?
fprintf(stderr,"Document not parsed successfully. \n");?
return (NULL);?
}?
cur = xmlDocGetRootElement(doc);?
if (cur == NULL) {?
fprintf(stderr,"empty document\n");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return (NULL);?
}?
if (xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *) "story")) {?
fprintf(stderr,"document of the wrong type, root node != story");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return (NULL);?
}?
cur = cur->xmlChildrenNode;?
while (cur != NULL) {?
if ((!xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *)"storyinfo"))){?
parseStory (doc, cur, keyword);?
}?
cur = cur->next;?
}?
return(doc);?
}?
int?
main(int argc, char **argv) {?
char *docname;?
char *keyword;?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
if (argc ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
xmlDocPtr?
parseDoc(char *docname, char *uri) {?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
xmlNodePtr cur;?
xmlNodePtr newnode;?
xmlAttrPtr newattr;?
doc = xmlParseFile(docname);?
if (doc == NULL ) {?
fprintf(stderr,"Document not parsed successfully. \n");?
return (NULL);?
}?
cur = xmlDocGetRootElement(doc);?
if (cur == NULL) {?
fprintf(stderr,"empty document\n");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return (NULL);?
}?
if (xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *) "story")) {?
fprintf(stderr,"document of the wrong type, root node != story");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return (NULL);?
}?
newnode = xmlNewTextChild (cur, NULL, "reference", NULL);?
newattr = xmlNewProp (newnode, "uri", uri);?
return(doc);?
}?
int?
main(int argc, char **argv) {?
char *docname;?
char *uri;?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
if (argc ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
#include ?
void?
getReference (xmlDocPtr doc, xmlNodePtr cur) {?
xmlChar *uri;?
cur = cur->xmlChildrenNode;?
while (cur != NULL) {?
if ((!xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *)"reference"))) {?
uri = xmlGetProp(cur, "uri");?
printf("uri: %s\n", uri);?
xmlFree(uri);?
}?
cur = cur->next;?
}?
return;?
}?
void?
parseDoc(char *docname) {?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
xmlNodePtr cur;?
doc = xmlParseFile(docname);?
if (doc == NULL ) {?
fprintf(stderr,"Document not parsed successfully. \n");?
return;?
}?
cur = xmlDocGetRootElement(doc);?
if (cur == NULL) {?
fprintf(stderr,"empty document\n");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
} ??
if (xmlStrcmp(cur->name, (const xmlChar *) "story")) {?
fprintf(stderr,"document of the wrong type, root node != story");?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
}?
getReference (doc, cur);?
xmlFreeDoc(doc);?
return;?
}?
int?
main(int argc, char **argv) {?
char *docname;?
if (argc ?
#include ?
unsigned char*?
convert (unsigned char *in, char *encoding)?
{?
unsigned char *out;?
int ret,size,out_size,temp;?
xmlCharEncodingHandlerPtr handler;?
size = (int)strlen(in)+1;?
out_size = size*2-1;?
out = malloc((size_t)out_size);?
if (out) {?
handler = xmlFindCharEncodingHandler(encoding);?
if (!handler) {?
free(out);?
out = NULL;?
}?
}?
if (out) {?
temp=size-1;?
ret = handler->input(out, &out_size, in, &temp);?
if (ret || temp-size+1) {?
if (ret) { ??
printf("conversion wasn’t successful.\n");?
} else {?
printf("conversion wasn’t successful. converted: }?
free(out);?
out = NULL;?
} else {?
out = realloc(out,out_size+1);?
out[out_size]=0; /*null terminating out*/?
}?
} else {?
printf("no mem\n");?
}?
return (out);?
}?
int?
main(int argc, char **argv) {?
unsigned char *content, *out;?
xmlDocPtr doc;?
xmlNodePtr rootnode;?
char *encoding = "ISO-8859-1";?
if (argc?
char *convert(char *instr,char *encoding)?
{?
xmlCharEncodingHandlerPtr handler;?
xmlBufferPtr in,out;?
handler = xmlFindCharEncodingHandler(encoding);?
if(NULL != handler)?
{?
in = xmlBufferCreate();?
xmlBufferWriteChar(in,instr);?
out = xmlBufferCreate();?
if(xmlCharEncInFunc(handler, out, in) 〈 0)?
{?
xmlBufferFree(in);?
xmlBufferFree(out);?
return NULL;?
}?
else?
{?
xmlBufferFree(in);?
return (char *)out-〉content;?
}?
}?
}
?